
The “anatomical” dead space is commonly measured by sampling an inert gas (N2) and volume in the exhalation following a large breath of oxygen (VD(F)). Alveolar dead space is the volume of air that fills the gas exchanging regions of the lung but does not participate in gas exchange. Physiological dead space is the combination of anatomical dead space plus alveolar dead space. What is the difference between anatomical and alveolar dead space?Īnatomical dead space is the volume of air that is in the conducting zone of the lung. The main difference between the shunt and dead space is that shunt is the pathological condition in which the alveoli are perfused but not ventilated, whereas dead space is the physiological condition in which the alveoli are ventilated but not perfused.
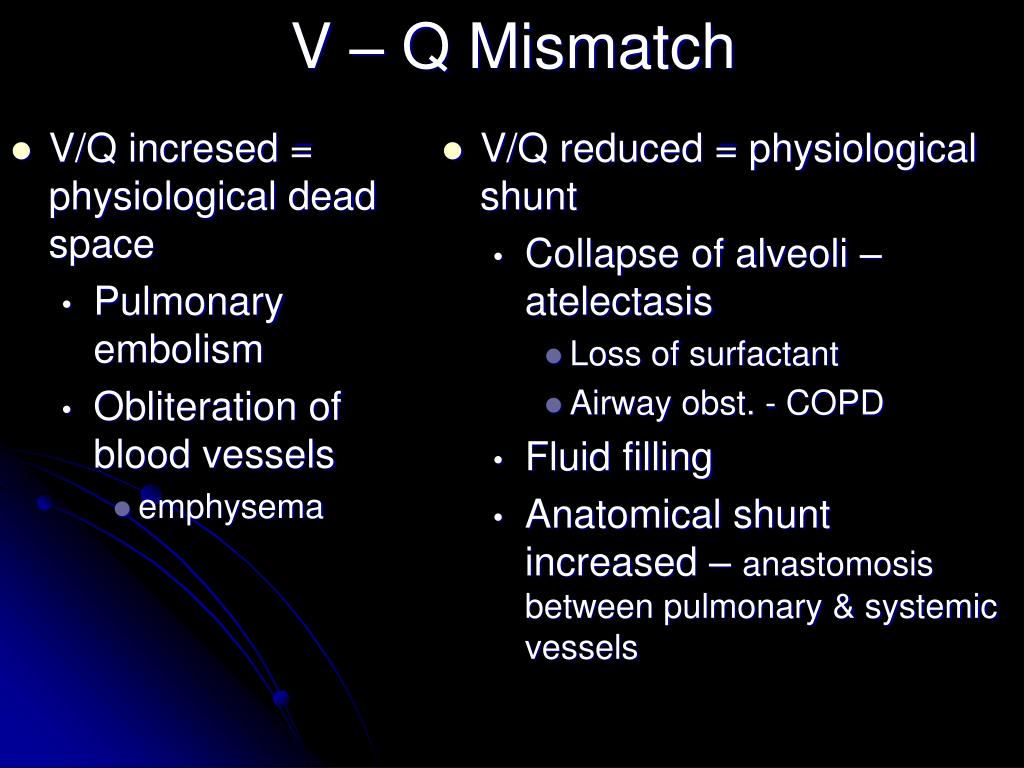
What is the difference between shunt and dead space?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
